Please Refer to “Create a simple spring boot application” for creating the first project and then we will work on customizing it.
Once the project is created and the tomcat server is starting, we will start writing our code to return custom message from spring boot controller and display it on browser.
Form the URL to test to view the custom message
Let’s add a functionality to display a message on hitting an URL.
The URL can be: – http://localhost:8080/welcome-message
** As you are running on your machine and opening the browser from the same, so we use localhost (127.0.0.1)
** By default the server starts on port 8080. If you change the port by updating application.yml, then update the port accordingly.
Let’s start the server and hit the URL on browser
We are getting a page as below.
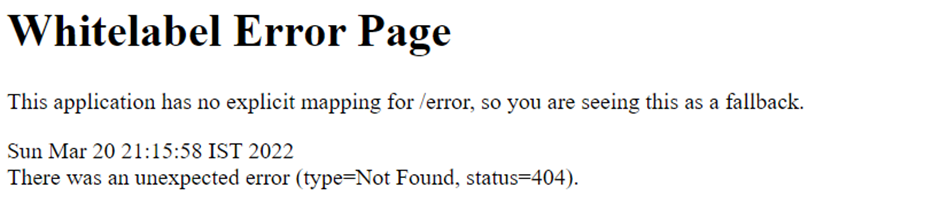
What is Whitelabel Error Page in Spring boot? Where is this coming from?
This is the default error page of Spring boot. As we have not created any custom error page, so Spring boot is showing an error page of its own. As we are hitting this URL, we have the server running but Spring boot is not able to find any page mapped to URI “welcome-message”.
So, let’s create it.
Step 1: Creating the Controller
Controller is a class which is checked by Spring boot to find the mapped URI. It has the required annotations. I am creating the controller named MessageController.java and creating a method named showWelcomeMessage.
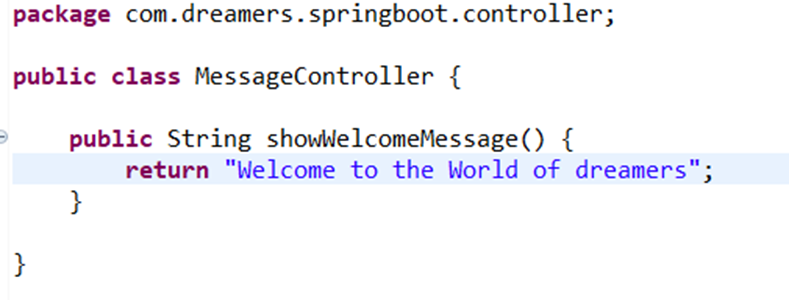
A very simple class with a method just returning a single line. Will it work? Let’s check out. Just think that you are hitting the URL mentioned above from your favourite browser. How will Spring Boot know that you want to call this method and return this string. You can have multiple methods and they might return different Strings. So, what should we do?
Step 2: Add @RequestMapping annotation
We need to tell Spring boot that our method showWelcomeMessage will be called when the URI have “welcome-message”. To do this, we can use a Spring Boot annotation – @RequestMapping as below.

Still, we are getting Whitelabel Error page. Why it is so? Now we have mapped the method to the URI. But Spring boot do not even know that this class is the controller class and it have to look here for the @RequestMapping annotation.
Step 3: Add @Controller annotation
This is one of the four most important class level annotations of Spring Boot. It would be added on top of the controller class as below and the server to be restarted. We will discuss about the other class level annotations in the respective sections.
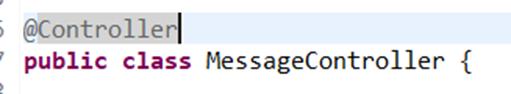
Still, we are getting the same error. What else is needed? If we enable debug level logging for org.springframework.web, then we can get some more details in the log about the issue.
How to enable debug level logging?
We need to add a string in application.yml or application.properties to configure debug level logging for the package. We can enable it for entire application, by just writing
logging.level: DEBUG (application.yml)
logging.level= DEBUG (application.properties)
but that will produce huge volume of log and would be difficult to go through. So, we are just enabling it for a single package as below

Once the change is done, we have to restart the server so that the change takes effect. Now if we hit the URL again, we are getting some more logs.

What is it looking for? Basically, DispatcherServlet considers the string returned by the method as a view name and looks for it. It is not able to understand that in this case whatever string we are returning, we just want the string to be the body of the response and not the view name.
Step 4: Add @ResponseBody annotation
To resolve the above issue, we must tell DispatcherServlet that whatever string we are returning is not a view name. It is just a string which will be the body of response. To do this, we just need to add a simple annotation @ResponseBody on top of the method and restart the server.
Now again hit the URL Yeah!! We got our message on the browser.

Conclusion
So, in this step, we learnt :
- What is the use of a controller class?
- How to tell dispatcher servlet, which class and method to check for a given URL?
- Various annotations like @Controller, @RequestMapping and @ResponseBody.
- How to change logging level?
Appendix
| URL for displaying welcome message | http://localhost:8080/welcome-message |
| Enabling logging for all (application.yml) | logging.level: DEBUG |
| Enabling logging for all (application.properties) | logging.level= DEBUG |
One thought on “How to return custom message from spring boot controller in just 4 steps”
I know this web page presents quality depending articles and additional data, is there any
other web site which offers such data in quality?